What Are Dm

In the world of data management and analysis, the term "DM" stands for Data Management, a critical discipline that forms the backbone of many industries and organizations. Data Management encompasses a wide range of processes and practices aimed at efficiently collecting, storing, organizing, and maintaining data to ensure its accessibility, reliability, and integrity. With the exponential growth of data in the digital age, effective Data Management has become an indispensable tool for businesses and researchers alike.
The Evolution of Data Management
Data Management is not a new concept, but its importance and scope have evolved significantly over the years. The journey began with the need to organize and store data in early computing systems, primarily for record-keeping and basic analytics. As technology advanced, so did the volume and complexity of data, leading to the development of sophisticated Data Management systems and practices.
Today, Data Management is a critical component of modern businesses, influencing decision-making, strategic planning, and operational efficiency. With the advent of big data and advanced analytics, the role of Data Management has expanded to support a wide range of applications, from predictive modeling and machine learning to real-time data analysis and visualization.
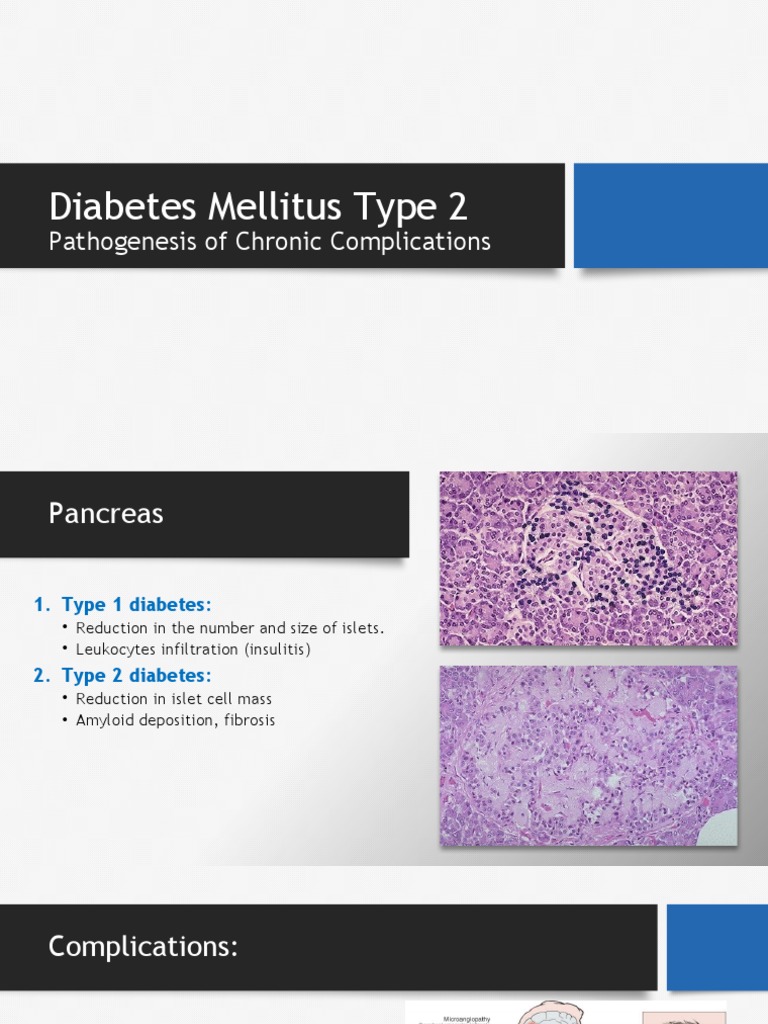
Key Components of Data Management
Data Management involves a multitude of interrelated processes, each playing a crucial role in the data lifecycle. Here are some of the key components:
- Data Collection: This is the initial stage where data is gathered from various sources, such as databases, sensors, user interactions, and external feeds. Effective data collection ensures that relevant and reliable data is available for analysis.
- Data Storage and Warehousing: Once collected, data needs to be stored securely and efficiently. Data warehouses and modern cloud-based storage solutions play a vital role in this process, providing scalable and accessible storage environments.
- Data Cleaning and Preparation: Raw data often contains errors, inconsistencies, and irrelevant information. Data cleaning and preparation techniques are used to transform data into a usable format, ensuring accuracy and completeness.
- Data Organization and Structure: Proper organization of data is essential for efficient retrieval and analysis. This involves defining data models, establishing relationships between data entities, and creating a logical data architecture.
- Data Security and Privacy: With the increasing importance of data protection and privacy regulations, Data Management must incorporate robust security measures to safeguard sensitive information. This includes encryption, access controls, and data anonymization techniques.
- Data Governance: Data governance involves the overall management and control of data assets within an organization. It ensures data is used consistently, efficiently, and in compliance with policies and regulations.
- Data Analysis and Reporting: Data Management supports various analytical processes, from basic reporting and business intelligence to advanced analytics and machine learning. The goal is to extract meaningful insights and support decision-making.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Data Collection | Gathering data from diverse sources for analysis. |
| Data Storage | Secure and scalable storage solutions for large datasets. |
| Data Cleaning | Transforming raw data into usable, accurate information. |
| Data Organization | Establishing logical structures and relationships for efficient retrieval. |
| Data Security | Protecting sensitive data through encryption and access controls. |
| Data Governance | Managing and controlling data assets for consistent usage. |
| Data Analysis | Extracting insights and supporting decision-making through analytics. |

Challenges and Future Prospects
While Data Management has advanced significantly, it continues to face challenges, particularly in the context of big data and evolving technologies. Some key challenges include:
- Data Volume and Velocity: The sheer volume and speed at which data is generated present significant challenges in terms of storage, processing, and analysis.
- Data Variety: Modern data comes in various formats and structures, from structured data in databases to semi-structured data in logs and unstructured data in documents and images. Managing and analyzing this diverse data requires specialized tools and techniques.
- Data Quality: Ensuring data quality and accuracy is a critical aspect of Data Management. Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to flawed insights and decision-making.
- Data Privacy and Security: With increasing concerns around data breaches and privacy violations, Data Management must incorporate robust security measures and adhere to strict privacy regulations.
- Data Integration: Integrating data from disparate sources and systems is a complex task, requiring careful planning and execution to ensure consistency and compatibility.
Future Prospects
Despite these challenges, the future of Data Management looks promising, driven by advancements in technology and a growing awareness of the value of data. Some key trends and prospects include:
- Advanced Analytics: Data Management will continue to support advanced analytical techniques, such as machine learning and artificial intelligence, to extract deeper insights from data.
- Real-time Data Processing: The ability to process and analyze data in real-time will become increasingly important, enabling organizations to respond quickly to changing market dynamics and customer needs.
- Data Democratization: With the rise of self-service analytics and business intelligence tools, Data Management will play a crucial role in empowering non-technical users to access and analyze data, driving data-driven decision-making across organizations.
- Cloud-based Data Management: Cloud computing offers significant advantages for Data Management, including scalability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency. Cloud-based solutions will continue to gain traction, especially for big data analytics and machine learning applications.
- Data Ethics and Governance: As data becomes a critical asset, ethical considerations and data governance will take center stage. Data Management professionals will need to ensure data is used responsibly and ethically, in line with organizational values and legal requirements.
What are the key benefits of effective Data Management?
+Effective Data Management offers numerous benefits, including improved decision-making through data-driven insights, enhanced operational efficiency, and better customer understanding. It also helps organizations stay compliant with regulations and reduces the risk of data breaches.
How can Data Management support business growth and innovation?
+Data Management provides the foundation for analytics and innovation. By collecting, organizing, and analyzing data, businesses can identify new opportunities, develop innovative products and services, and optimize existing processes.
What are some best practices for Data Management?
+Best practices include defining clear data governance policies, implementing robust data security measures, ensuring data quality, and providing training and support for data management tools and processes.



