The Worm's Secretive Reproduction Process

Unveiling the mysteries of nature often leads us to intriguing discoveries, and today, we delve into the fascinating world of the worm's reproductive process. These humble creatures, often overlooked, possess a unique and somewhat enigmatic approach to reproduction. Let's embark on a journey to understand the intricacies of how worms perpetuate their species, a process that is both intriguing and essential to the balance of ecosystems worldwide.
The Worm’s Unique Reproductive Strategy

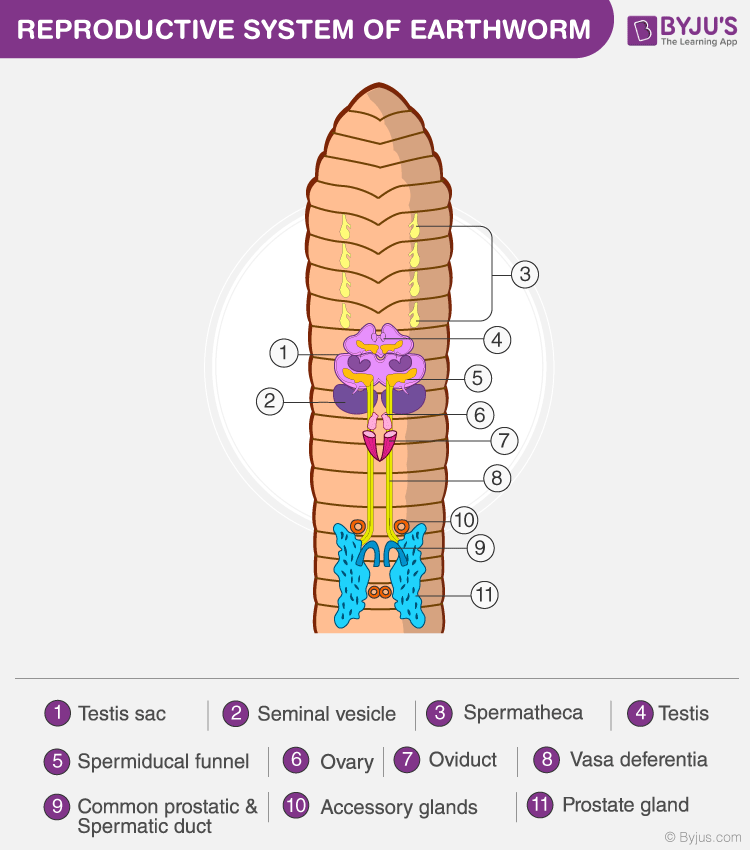
Worms, belonging to the phylum Annelida, employ a reproductive strategy that is markedly different from many other organisms. Unlike most animals, worms are hermaphrodites, possessing both male and female reproductive organs. This adaptation allows them to reproduce both sexually and asexually, a unique ability that ensures their survival and genetic diversity.
Sexual Reproduction: A Mating Ritual
During sexual reproduction, worms engage in a fascinating mating ritual. Two worms align their bodies, with their heads pointing in opposite directions, forming a heart-shaped configuration. This intimate embrace allows for the exchange of genetic material. Each worm contributes sperm and receives eggs, ensuring the creation of offspring with a unique genetic makeup.
This process is facilitated by a special structure called the clitellum, a thick, glandular band located near the worm's anterior end. The clitellum secretes a mucus tube that envelops the worms' genital openings, creating a chamber for sperm exchange. Once the tube is filled with sperm, it slips off the worms, providing a protective environment for the developing eggs.
| Reproduction Mode | Description |
|---|---|
| Sexual | Involves two worms exchanging genetic material through a mucus tube secreted by the clitellum. |
| Asexual | Occurs when a single worm fragments, with each fragment growing into a new individual. |
Asexual Reproduction: The Power of Fragmentation
In addition to their sexual prowess, worms can reproduce asexually through a process called fragmentation. This remarkable ability allows a single worm to divide into multiple segments, with each segment capable of growing into a new, fully functional individual. This process is particularly advantageous in environments where finding a mate may be challenging.
When a worm fragments, it carefully regulates the process to ensure that each new segment contains all the necessary organs and systems to survive. This includes the vital clitellum, ensuring that the newly formed worms can reproduce sexually when the time is right. Fragmentation is a rapid and effective way for worms to increase their population, especially in favorable conditions.
The Role of Worms in Ecosystems

Worms play an indispensable role in various ecosystems, particularly in soil health and nutrient cycling. Their unique reproductive strategies contribute significantly to the balance and resilience of these environments.
Soil Health and Nutrient Cycling
Through their feeding and burrowing activities, worms aerate and mix soil, improving its structure and promoting better drainage. This process also enhances nutrient availability, as worms break down organic matter, making essential nutrients more accessible to plants. Additionally, worm castings, or their excretions, are rich in nutrients, further enhancing soil fertility.
Impact on Biodiversity
The presence of worms in an ecosystem fosters biodiversity. Their activities create microhabitats and improve soil conditions, attracting a variety of organisms. This can lead to a more complex and resilient food web, enhancing the overall health and stability of the ecosystem.
The Worm’s Adaptability and Resilience
The worm’s unique reproductive capabilities are a testament to their adaptability and resilience. By combining sexual and asexual reproduction, they can respond effectively to changing environmental conditions and maintain genetic diversity. This flexibility allows them to thrive in a wide range of habitats, from gardens to aquatic environments.
Environmental Adaptability
Worms are found in diverse environments, from forests and grasslands to freshwater and marine habitats. Their ability to reproduce through fragmentation enables them to rapidly colonize new areas and adapt to changing conditions. This adaptability ensures their survival and continued contribution to ecosystem health.
Genetic Diversity and Survival
The worm’s hermaphroditic nature and ability to reproduce sexually ensures genetic diversity within their populations. This diversity is crucial for long-term survival, as it allows for the development of traits that may be advantageous in changing environmental conditions. By combining genetic material from different individuals, worms can pass on beneficial traits to their offspring, enhancing their ability to withstand environmental challenges.
Conclusion: The Enigmatic World of Worm Reproduction
The worm’s reproductive process is a fascinating and intricate dance of nature. Through their unique abilities to reproduce both sexually and asexually, worms have ensured their survival and ecological significance. Their role in soil health, nutrient cycling, and biodiversity is vital, making them an indispensable part of the natural world.
As we uncover the secrets of these humble creatures, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complex and often hidden processes that sustain life on our planet. The worm's story is a reminder of the beauty and resilience found in the most unassuming of creatures.
How do worms contribute to soil health?
+Worms improve soil health by aerating and mixing the soil, enhancing drainage, and making nutrients more accessible to plants. Their feeding and burrowing activities create a more fertile and vibrant soil ecosystem.
Can worms reproduce without a mate?
+Yes, worms can reproduce asexually through fragmentation. This process allows a single worm to divide into multiple segments, each capable of growing into a new individual.
What is the role of the clitellum in worm reproduction?
+The clitellum is a specialized structure that secretes a mucus tube for sperm exchange during sexual reproduction. It provides a protective environment for the developing eggs, ensuring the successful creation of offspring.



