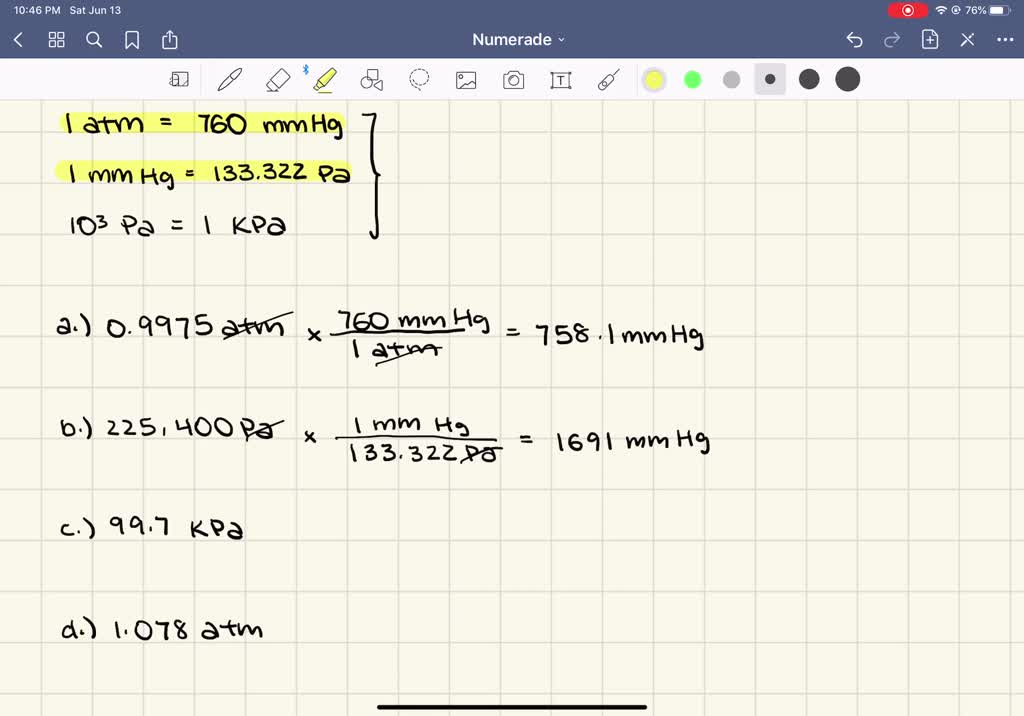
Convert mmHg: 5 Quick Steps

Understanding and converting blood pressure measurements is an essential skill for anyone interested in health and fitness. The unit millimeters of mercury (mmHg) is commonly used to express blood pressure, but it can be unfamiliar and confusing for those who are not in the medical field. In this guide, we will break down the process of converting mmHg into simpler terms, making it easier for you to interpret and monitor your blood pressure effectively.
What is mmHg?
Millimeters of mercury, or mmHg, is a unit of measurement used to express pressure, specifically in the context of blood pressure readings. It represents the pressure exerted by a column of mercury, which was historically used in early blood pressure measurement devices. While mercury-based instruments are less common nowadays, the unit mmHg remains widely used to standardize blood pressure measurements.
Blood pressure is typically recorded as two values: the systolic pressure (the higher number) and the diastolic pressure (the lower number). For example, a blood pressure reading of 120/80 mmHg indicates a systolic pressure of 120 mmHg and a diastolic pressure of 80 mmHg. These values provide crucial insights into the health of your cardiovascular system.
Step 1: Understand the Blood Pressure Categories
Before diving into the conversion process, it’s essential to familiarize yourself with the different blood pressure categories. These categories help healthcare professionals and individuals assess their cardiovascular health and take appropriate measures.
| Blood Pressure Category | Systolic (mmHg) | Diastolic (mmHg) |
|---|---|---|
| Normal | 90-120 | 60-80 |
| Elevated | 120-129 | 80-89 |
| Hypertension Stage 1 | 130-139 | 80-99 |
| Hypertension Stage 2 | 140 or higher | 90 or higher |
| Hypertensive Crisis | 180 or higher | 120 or higher |
Normal Blood Pressure
A blood pressure reading within the normal range indicates a healthy cardiovascular system. It’s important to maintain this range through regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management.
Elevated Blood Pressure
When blood pressure readings consistently fall into the elevated category, it’s a warning sign that you may be at risk of developing hypertension. Lifestyle changes and regular monitoring are recommended to prevent further complications.
Hypertension
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a serious condition that can lead to various health issues, including heart disease and stroke. If your blood pressure readings indicate hypertension, consult with a healthcare professional for guidance and treatment options.
Step 2: Gather the Necessary Tools
To convert mmHg readings accurately, you’ll need a few simple tools. Here’s what you’ll require:
- A blood pressure monitor: Choose a reliable monitor that provides accurate readings. Digital monitors are user-friendly and widely available.
- A conversion chart or calculator: While not necessary, having a conversion chart or an online calculator can make the process quicker and more convenient.
- A notepad and pen: Keep track of your blood pressure readings and any notes you want to make about your cardiovascular health.
Step 3: Measure Your Blood Pressure
The first step in converting mmHg is to measure your blood pressure accurately. Follow these guidelines to ensure precise readings:
- Find a quiet and comfortable environment to take your blood pressure.
- Sit upright with your back supported and your legs uncrossed.
- Rest for at least 5 minutes before taking the measurement to ensure an accurate reading.
- Place the blood pressure cuff on your upper arm, ensuring it fits snugly but not too tightly.
- Follow the instructions provided with your blood pressure monitor to obtain your systolic and diastolic pressure readings.
Interpreting Your Blood Pressure Readings
Once you have your blood pressure readings, you can determine whether they fall within a healthy range or if they indicate any potential concerns. Compare your readings to the blood pressure categories mentioned earlier to assess your cardiovascular health.
Step 4: Convert mmHg to Your Preferred Unit

Now that you have your blood pressure readings in mmHg, you might want to convert them to a unit that is more familiar to you. Here’s how to do it:
Converting mmHg to KPa (Kilopascals)
Kilopascals (kPa) is a commonly used unit for pressure measurements. To convert mmHg to kPa, use the following formula:
kPa = mmHg * 0.1333
For example, if your systolic pressure is 120 mmHg, the conversion would be:
kPa = 120 mmHg * 0.1333 = 16 kPa
Converting mmHg to psi (Pounds per Square Inch)
Pounds per square inch (psi) is another unit of pressure measurement. To convert mmHg to psi, use the following formula:
psi = mmHg * 0.01316
Let's take the same example: if your systolic pressure is 120 mmHg, the conversion would be:
psi = 120 mmHg * 0.01316 = 1.5792 psi
Converting mmHg to bar (Atmospheres)
The bar (atmosphere) is a metric unit for pressure. To convert mmHg to bar, use the following formula:
bar = mmHg * 0.001333
Using our previous example, the conversion for a systolic pressure of 120 mmHg would be:
bar = 120 mmHg * 0.001333 = 0.15996 bar
Step 5: Monitor and Maintain Healthy Blood Pressure
Understanding and converting your blood pressure readings is just the first step. The real goal is to maintain a healthy blood pressure range and ensure the well-being of your cardiovascular system. Here are some tips to help you achieve this:
- Adopt a heart-healthy diet: Focus on eating plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Reduce your intake of processed foods, salt, and saturated fats.
- Exercise regularly: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity activity per week. Combine this with strength training exercises for optimal cardiovascular health.
- Manage stress: Chronic stress can contribute to high blood pressure. Practice relaxation techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, or yoga to keep your stress levels in check.
- Limit alcohol consumption: Excessive alcohol intake can raise blood pressure. Stick to moderate drinking or consider cutting back if you struggle with high blood pressure.
- Quit smoking: Smoking is a major risk factor for high blood pressure and cardiovascular disease. Seek support and resources to help you quit smoking for good.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Being overweight or obese can increase your risk of high blood pressure. Aim for a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise.
- Monitor your blood pressure regularly: Track your blood pressure readings over time to identify any trends or changes. Share this information with your healthcare provider for further guidance.
When to Consult a Healthcare Professional
If you have consistently high blood pressure readings or if you experience symptoms such as headaches, dizziness, or shortness of breath, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional. They can provide a thorough assessment, recommend lifestyle changes, and prescribe medications if necessary.
Conclusion
Understanding and converting blood pressure measurements in mmHg is a valuable skill for anyone interested in their cardiovascular health. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can accurately interpret your blood pressure readings and take proactive steps to maintain a healthy cardiovascular system. Remember, knowledge is power, and by taking control of your blood pressure, you’re taking a significant step towards a healthier and happier life.
Why is it important to understand blood pressure measurements in mmHg?
+Understanding blood pressure measurements in mmHg allows individuals to monitor their cardiovascular health and make informed decisions about their lifestyle and well-being. It helps identify potential health risks and encourages proactive measures to maintain a healthy blood pressure range.
What are the common blood pressure categories, and how do they impact my health?
+Blood pressure categories include normal, elevated, hypertension stage 1, hypertension stage 2, and hypertensive crisis. Each category indicates a different level of cardiovascular health. Normal blood pressure is ideal, while elevated and hypertension stages indicate potential health risks and the need for lifestyle changes or medical intervention.
Can I use a manual blood pressure cuff to measure my blood pressure accurately?
+While manual blood pressure cuffs can provide accurate readings, they require proper technique and training. Digital blood pressure monitors are often more user-friendly and provide precise measurements. If you prefer a manual cuff, ensure you receive proper instruction on its use.
How often should I measure my blood pressure, and what is considered a healthy range?
+It’s recommended to measure your blood pressure at least once a month, or more frequently if advised by your healthcare provider. A healthy blood pressure range is typically considered to be below 120⁄80 mmHg. However, it’s important to monitor your readings over time and discuss any concerns with your healthcare professional.



