Strategies for Improving Impaired Gas Exchange
Impaired gas exchange is a critical health issue that affects countless individuals worldwide, hindering their ability to breathe effectively and efficiently. This condition can arise from various factors, including respiratory diseases, lung injuries, or even environmental pollutants. Fortunately, there are strategies and interventions that can help mitigate the impact of impaired gas exchange, improving the quality of life for those affected.
Understanding Impaired Gas Exchange

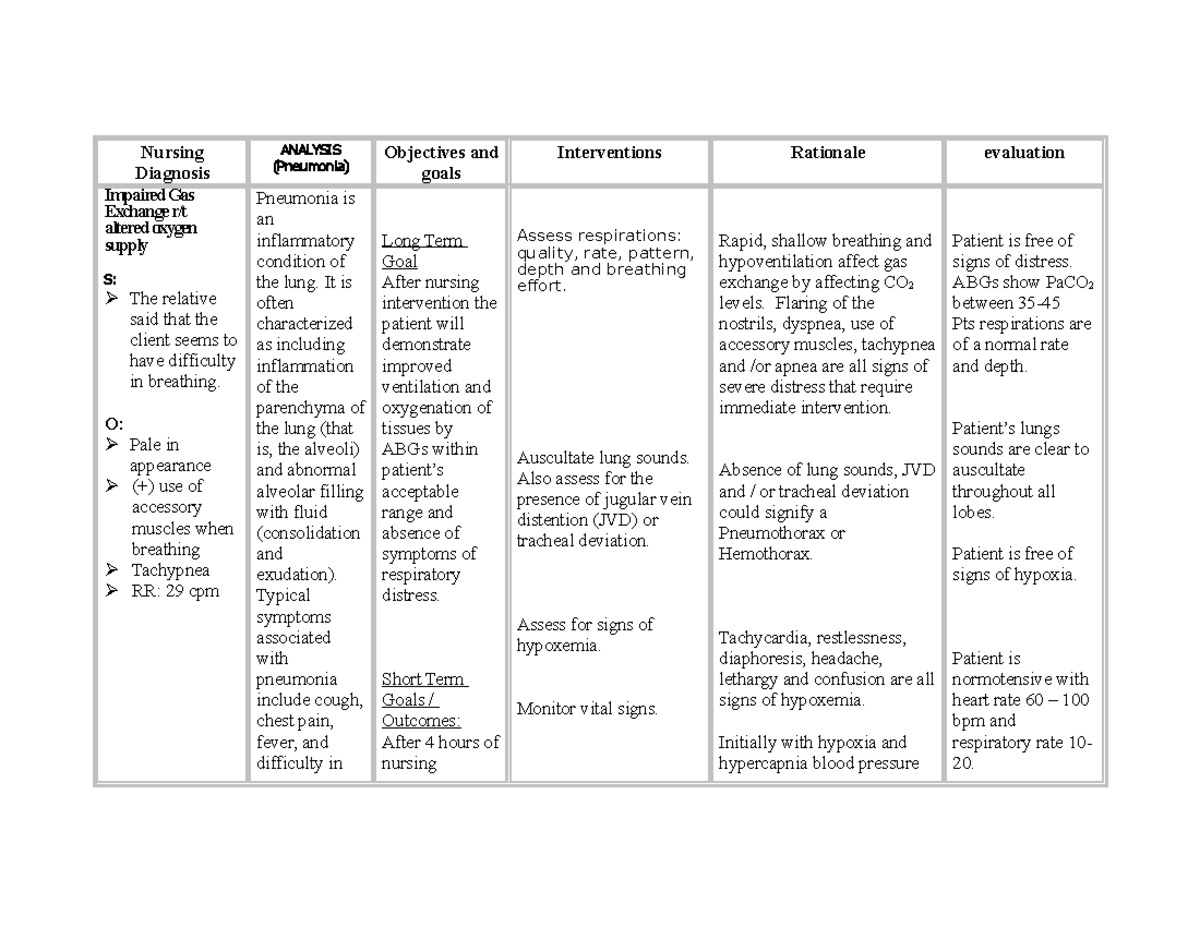
Impaired gas exchange refers to the inability of the lungs to adequately facilitate the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the alveolar spaces and the bloodstream. This vital process is crucial for sustaining life, as it ensures the body receives the necessary oxygen for cellular function and removes waste products like carbon dioxide. When this exchange is compromised, it can lead to a range of health complications, including shortness of breath, fatigue, and even organ damage if left untreated.
The causes of impaired gas exchange are diverse and can include:
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
- Asthma
- Pneumonia
- Lung injuries due to trauma or infection
- Environmental factors such as air pollution or occupational hazards
- Certain medications or medical conditions that affect lung function
Strategies for Improvement

Improving impaired gas exchange requires a multifaceted approach that addresses the underlying causes and provides effective interventions. Here are some key strategies and techniques that can aid in the management and improvement of this condition:
Medications and Therapy
Pharmacological interventions play a vital role in managing impaired gas exchange. Depending on the underlying cause, healthcare professionals may prescribe medications such as bronchodilators, corticosteroids, or antibiotics. These medications help relax the airways, reduce inflammation, and combat infections, thereby improving gas exchange.
In addition to medications, respiratory therapy is often recommended. Respiratory therapists can provide guidance on breathing techniques, such as pursed-lip breathing or diaphragm breathing, which can help optimize lung function and improve gas exchange. These techniques can be particularly beneficial for individuals with chronic respiratory conditions.
Pulmonary Rehabilitation
Pulmonary rehabilitation is a comprehensive program designed to improve lung function and enhance the overall quality of life for individuals with respiratory conditions. This program typically includes a combination of exercise training, education, and behavioral interventions.
Exercise training in pulmonary rehabilitation focuses on improving cardiovascular fitness, muscle strength, and endurance. It often involves a tailored exercise regimen that includes activities like walking, cycling, or swimming, which can be adjusted based on the individual's capabilities and preferences. Regular exercise helps improve lung capacity, oxygen uptake, and overall physical endurance.
Educational components of pulmonary rehabilitation aim to empower individuals with knowledge about their condition, medications, and self-management strategies. Understanding the disease process and learning effective coping mechanisms can help patients take an active role in their care and make informed decisions about their health.
Lifestyle Modifications
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly impact lung function and gas exchange. Here are some key lifestyle modifications that can contribute to improvement:
- Smoking Cessation: Smoking is a major risk factor for respiratory diseases and impaired gas exchange. Quitting smoking is one of the most effective ways to improve lung health and overall well-being. Smoking cessation programs and support groups can provide valuable assistance in this process.
- Healthy Diet: Maintaining a nutritious diet can support lung health. Foods rich in antioxidants, such as fruits and vegetables, can help reduce inflammation and promote respiratory health. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish and nuts, have also been associated with improved lung function.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity, beyond the context of pulmonary rehabilitation, is beneficial for lung function. Activities like yoga, swimming, or even brisk walking can help strengthen respiratory muscles and improve gas exchange.
- Avoiding Environmental Triggers: Identifying and minimizing exposure to environmental triggers, such as air pollution, allergens, or occupational hazards, can help prevent exacerbations of impaired gas exchange. Using air purifiers, wearing protective gear, and avoiding high-pollution areas can all contribute to better respiratory health.
Oxygen Therapy
For individuals with severe impaired gas exchange, oxygen therapy may be necessary. This involves the administration of supplemental oxygen to help meet the body’s oxygen demands. Oxygen therapy can be delivered through various methods, such as nasal cannulas, face masks, or portable oxygen concentrators.
Oxygen therapy is often used in acute settings, such as during an exacerbation of a respiratory condition, or on a long-term basis for individuals with chronic lung diseases. It helps improve oxygen levels in the blood, alleviating symptoms like shortness of breath and reducing the risk of further complications.
Surgical Interventions
In certain cases, surgical interventions may be considered to improve impaired gas exchange. For example, lung volume reduction surgery is sometimes recommended for individuals with severe emphysema, a type of COPD. This surgery involves removing damaged lung tissue to improve the function of the remaining healthy lung.
Another surgical option is lung transplantation, which is typically reserved for end-stage lung disease. While this procedure carries significant risks and requires lifelong immunosuppressive therapy, it can offer a new lease on life for individuals with severe, irreversible lung damage.
Performance Analysis and Future Implications
The effectiveness of these strategies in improving impaired gas exchange has been supported by numerous clinical studies and real-world outcomes. For instance, pulmonary rehabilitation programs have consistently shown improvements in lung function, exercise capacity, and quality of life for individuals with chronic respiratory conditions.
Additionally, the use of medications, particularly bronchodilators and corticosteroids, has been instrumental in managing acute exacerbations and reducing the frequency and severity of respiratory symptoms. These medications help relax the airways and reduce inflammation, thereby enhancing gas exchange.
Looking ahead, the future of impaired gas exchange management holds promising advancements. Ongoing research is focused on developing more targeted medications and therapies, such as novel bronchodilators and anti-inflammatory agents, which could further improve respiratory outcomes. Moreover, the integration of digital health technologies, like remote monitoring systems and wearable devices, may revolutionize the way impaired gas exchange is managed, providing real-time data and personalized interventions.
Furthermore, public health initiatives aimed at reducing environmental pollutants and promoting healthy lifestyles can play a crucial role in preventing and managing impaired gas exchange. By addressing the root causes and empowering individuals to take control of their respiratory health, we can strive towards a future where impaired gas exchange is effectively managed and the burden of respiratory diseases is significantly reduced.
| Strategy | Impact |
|---|---|
| Medications (Bronchodilators, Corticosteroids) | Reduced inflammation, improved airway relaxation, and enhanced gas exchange |
| Respiratory Therapy | Optimized breathing techniques, improved lung function, and increased quality of life |
| Pulmonary Rehabilitation | Enhanced cardiovascular fitness, muscle strength, and endurance; improved lung capacity and oxygen uptake |
| Lifestyle Modifications | Improved lung health through smoking cessation, healthy diet, regular exercise, and avoidance of environmental triggers |
| Oxygen Therapy | Increased oxygen levels in the blood, alleviated symptoms, and reduced complications |
| Surgical Interventions | Removed damaged lung tissue, improved lung function, and offered a new lease on life in severe cases |

How long does it take to see improvements with pulmonary rehabilitation?
+The timeline for improvements varies depending on the individual’s condition and the intensity of the pulmonary rehabilitation program. However, most individuals start noticing improvements in lung function, exercise capacity, and overall well-being within a few weeks to a few months of consistent participation in the program.
Are there any alternative therapies for impaired gas exchange?
+While alternative therapies, such as herbal remedies or acupuncture, may offer some symptom relief, it’s important to note that scientific evidence supporting their effectiveness in improving impaired gas exchange is limited. It’s always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before trying any alternative therapies.
Can impaired gas exchange be completely cured?
+The prognosis for impaired gas exchange depends on the underlying cause and the severity of the condition. While some conditions, such as acute respiratory infections, may resolve completely with appropriate treatment, chronic respiratory diseases like COPD are typically managed rather than cured. However, with effective management strategies, individuals can experience significant improvements in their symptoms and overall quality of life.