How To Use Blood Agar Plate Easy Culture Tips

In the world of microbiology, the ability to isolate and cultivate microorganisms is a fundamental skill. Blood agar plates are a common and invaluable tool in this process, offering a rich medium for the growth and observation of various bacterial species. This guide aims to provide an in-depth understanding of how to effectively utilize blood agar plates, offering tips and insights to ensure successful and informative culturing experiences.
Understanding Blood Agar Plates
Blood agar plates, or BPA (Blood Plate Agar), are a type of growth medium used in microbiology to cultivate fastidious organisms, especially those requiring a source of blood for growth, such as Streptococcus and Staphylococcus species. The medium is composed of a base of nutrient agar, supplemented with 5-10% sheep or horse blood, which is then poured into sterile petri dishes and allowed to solidify.
Composition and Preparation
The composition of blood agar is critical to its effectiveness. The base agar provides essential nutrients, while the addition of blood introduces key proteins and growth factors necessary for the survival and growth of certain bacteria. The blood is typically added to the agar in a liquid form, which is then mixed thoroughly before being poured into petri dishes. The plates are then left to solidify in a sterile environment, often at room temperature or in a 37°C incubator.
| Component | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Nutrient Agar | Provides essential nutrients for bacterial growth |
| Sheep/Horse Blood | Supplies necessary proteins and growth factors |
Types of Blood Agar
There are two main types of blood agar: tryptic soy agar (TSA) with 5% sheep blood and Columbia agar with 5% sheep blood. The choice between the two depends on the specific needs of the experiment or culturing process. TSA is a general-purpose medium that supports the growth of a wide range of microorganisms, while Columbia agar is often preferred for its ability to enhance the hemolytic patterns of certain bacteria, making it ideal for species identification.
Steps for Successful Culturing

The process of culturing bacteria on blood agar plates requires a systematic approach to ensure accurate results. Here are the key steps to follow, accompanied by some expert tips to enhance the success of your culturing endeavors.
Preparing the Work Area
Before beginning, it’s crucial to set up a clean and sterile workspace. This involves using disinfectant sprays or wipes to clean the bench area and any equipment that will be used. Sterilization is key to preventing contamination, which can significantly impact the accuracy of your results. Always work in a well-ventilated area, and if possible, use a laminar flow cabinet to maintain an even higher level of sterility.
Plating Techniques
When plating samples onto blood agar plates, there are several methods to consider, each with its advantages and applications.
- Streak Plate Method: This is a common technique used to isolate pure cultures. The sample is streaked across the plate in a zigzag pattern, with each pass reducing the number of bacteria transferred. This method allows for the growth of isolated colonies, making it easier to identify and select specific bacterial strains.
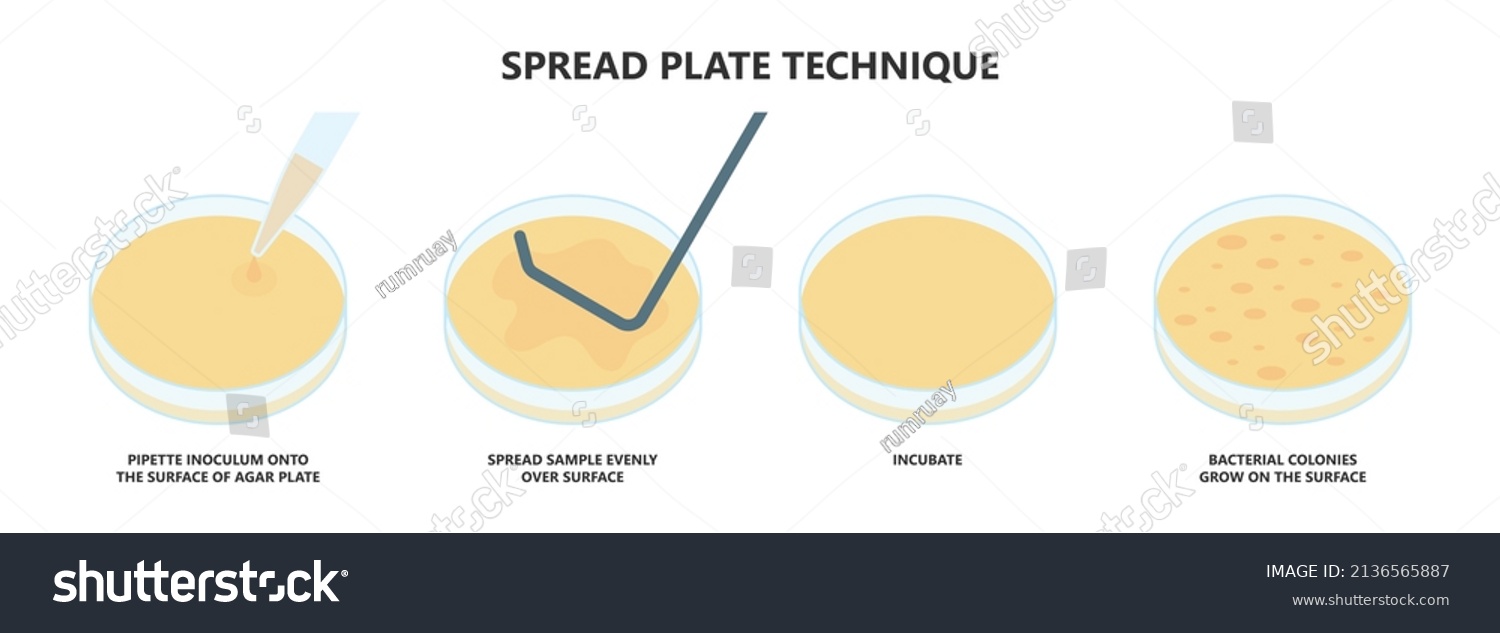
- Spread Plate Method: By using a sterile spreader, a uniform layer of bacteria can be applied across the entire plate. This method is often used for quantitative analysis, as it allows for the estimation of bacterial counts based on colony formation.
- Pour Plate Method: Here, the sample is mixed with molten agar, which is then poured into the petri dish. This method is useful for anaerobic bacteria or when you want to ensure the sample is evenly distributed throughout the medium.
Incubation and Observation
After plating, the blood agar plates are typically incubated at 37°C for 18-24 hours, although some bacteria may require different conditions. During incubation, it’s important to observe the plates at regular intervals to monitor the growth and characteristics of the colonies. Note any changes in color, texture, or the presence of hemolysis (the breakdown of red blood cells), as these can be indicative of specific bacterial species.
Interpreting Results
The interpretation of results from blood agar plates is a critical step in microbiology. The appearance of colonies, their morphology, and the patterns of hemolysis can provide valuable insights into the identity of the cultured bacteria. For instance, the presence of clear zones around colonies (beta-hemolysis) often indicates the activity of certain Streptococcus species, while a green discoloration (alpha-hemolysis) might suggest the presence of Staphylococcus aureus. Understanding these characteristics is key to accurate species identification.
Common Challenges and Troubleshooting
While blood agar plates are a powerful tool, they can present certain challenges. Here are some common issues and potential solutions to help you navigate these difficulties.
Contamination
Contamination is a frequent concern in microbiology. To minimize this risk, ensure a sterile work environment and use proper aseptic techniques. If contamination occurs, it’s often visible as an unexpected growth or discoloration on the plate. In such cases, it’s best to discard the plate and start the process again with more stringent sterility measures.
Slow or Inhibited Growth
Bacteria may sometimes grow slowly or not at all on blood agar plates. This could be due to several factors, including the age of the medium, incorrect storage conditions, or the specific requirements of the bacterial species. To address this, ensure fresh, properly prepared medium is used, and consider alternative growth conditions or media if growth remains inhibited.
Misinterpretation of Results
Interpreting results from blood agar plates requires a good understanding of bacterial characteristics. Misinterpretation can occur, especially with similar-looking colonies or when unfamiliar species are encountered. In such cases, it’s beneficial to refer to comprehensive guides or seek advice from more experienced microbiologists. Additionally, using multiple types of media or further biochemical tests can help confirm the identity of the cultured bacteria.
Advanced Techniques and Applications
Blood agar plates have a wide range of applications beyond basic culturing. Here are some advanced techniques and their potential uses.
Disc Diffusion Method
The disc diffusion method involves placing filter paper discs impregnated with antibiotics onto the surface of the blood agar plate, which has been inoculated with the test bacteria. After incubation, the plates are examined for zones of inhibition around the discs. This method is commonly used to determine the antibiotic sensitivity of bacteria, aiding in the selection of appropriate treatments for infections.
Blood Agar as a Diagnostic Tool
Blood agar plates can be an invaluable diagnostic tool in clinical microbiology. By culturing samples from patients, such as blood, urine, or sputum, on blood agar, microbiologists can identify the causative agents of infections. The morphology and characteristics of the colonies can provide crucial information for diagnosing and treating various diseases.
Research Applications
Blood agar plates are also widely used in research settings. They can be employed to study bacterial behavior, virulence factors, and antibiotic resistance. By manipulating the composition of the medium or the environmental conditions, researchers can gain insights into the mechanisms of bacterial growth and survival, contributing to the development of new treatments and strategies for combating infectious diseases.
Safety Considerations
Working with blood agar plates and bacterial cultures requires adherence to strict safety protocols. Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including lab coats, gloves, and eye protection. Dispose of used plates and equipment properly, following institutional guidelines for biohazardous waste. Additionally, be aware of the potential hazards associated with specific bacteria and take necessary precautions to prevent exposure or infection.
Conclusion
Blood agar plates are an indispensable tool in the field of microbiology, offering a rich and versatile medium for the cultivation and study of various bacterial species. By understanding their composition, preparation, and application, microbiologists can effectively utilize blood agar plates to isolate, identify, and study microorganisms. This guide has provided an in-depth look at the process, from preparation to interpretation, offering valuable insights and practical tips for successful culturing. With the right techniques and a systematic approach, blood agar plates can unlock a wealth of information about the microbial world.
What are the ideal incubation conditions for blood agar plates?
+Blood agar plates are typically incubated at 37°C for 18-24 hours. However, some bacterial species may require different conditions. For instance, certain anaerobic bacteria might need incubation in a CO2-enriched environment or under anaerobic conditions. Always refer to specific guidelines for the bacterial species you are culturing.
How can I ensure accurate results when interpreting hemolysis patterns on blood agar plates?
+Accurate interpretation of hemolysis patterns is crucial for species identification. It’s important to have a good understanding of the characteristic hemolysis patterns of common bacterial species. For example, complete breakdown of red blood cells (beta-hemolysis) often indicates the presence of certain Streptococcus species, while partial breakdown (alpha-hemolysis) might suggest Staphylococcus aureus. Referring to comprehensive guides and comparing with known reference strains can aid in accurate identification.
What should I do if I notice contamination on a blood agar plate during incubation?
+If you notice contamination on a blood agar plate during incubation, it’s best to discard the plate and start the process again with more stringent sterility measures. Contamination can significantly impact the accuracy of your results, so it’s important to maintain a sterile work environment and use proper aseptic techniques to minimize this risk.



