F22 Program Cost

The F-22 Raptor is a fifth-generation stealth fighter aircraft developed by Lockheed Martin and considered one of the most advanced and formidable combat jets in the world. Its development, production, and operational costs have been a subject of intense scrutiny and debate, especially considering the unique capabilities and technological advancements it brings to the United States Air Force.
Development and Early Costs
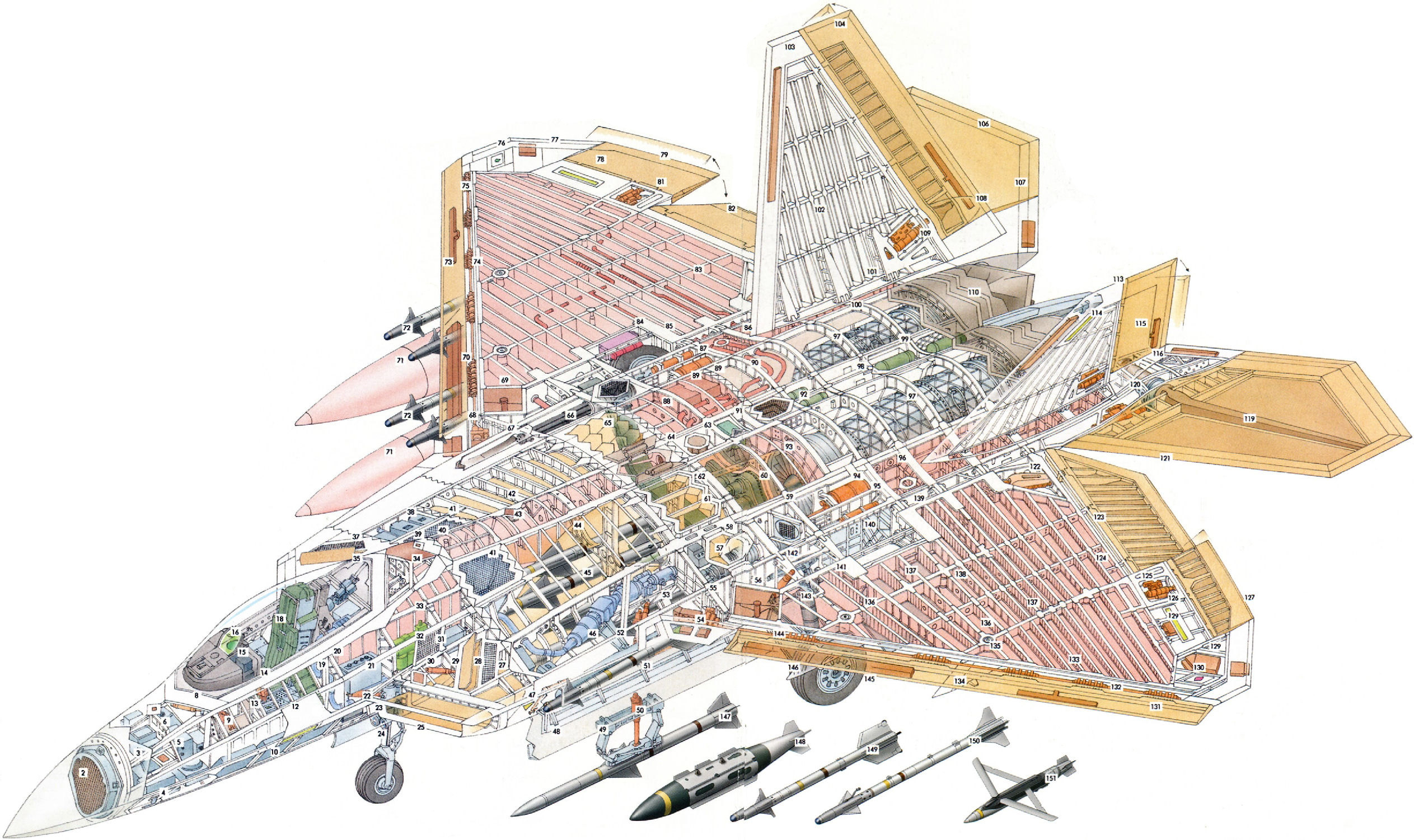
The origins of the F-22 can be traced back to the 1980s when the US Air Force initiated the Advanced Tactical Fighter (ATF) program to replace aging fighter aircraft. Lockheed Martin, in collaboration with Boeing and Pratt & Whitney, emerged as the winning team with their design, which eventually evolved into the F-22 Raptor.
The development phase, which spanned from 1986 to 1997, was marked by significant technological challenges and cost overruns. The aircraft's advanced stealth capabilities, supercruise (sustained supersonic flight without afterburners), and advanced avionics required extensive research and development. This period saw the program's costs escalate, and by the time the first production aircraft was delivered in 2003, the F-22 had become one of the most expensive military aircraft projects in history.
Key Cost Drivers During Development
- Stealth Technology: Achieving the F-22’s low observable or stealth characteristics required innovative materials and design, contributing significantly to the program’s cost.
- Advanced Avionics: The aircraft’s onboard computer systems and sensors, designed to process vast amounts of data in real-time, were cutting-edge and expensive to develop.
- Engine Development: The Pratt & Whitney F119 engines, capable of supercruise, were a major development effort, adding to the overall cost.
- Test and Evaluation: Rigorous testing to ensure the aircraft met its performance and stealth criteria was both time-consuming and costly.
| Development Cost (1986-1997) | $18 billion |
|---|---|
| Total Aircraft Produced | 195 |

Production and Procurement Costs

The production phase of the F-22 Raptor saw further cost increases, primarily due to the specialized nature of the aircraft and its components. Each F-22 required approximately 1 million labor hours to assemble, with many of the components produced in limited quantities, driving up costs.
Breakdown of Production Costs
- Materials and Components: The aircraft’s stealth materials, advanced alloys, and specialized avionics made up a significant portion of the production cost.
- Assembly and Testing: The intricate assembly process and rigorous testing procedures added to the overall expense.
- Overhead and Support Costs: These included costs for facilities, infrastructure, and the support staff required for production and maintenance.
| Average Cost per F-22 (Production Phase) | $150 million |
|---|---|
| Total Production Cost (1997-2011) | $27.3 billion |
Operational Costs
The operational costs of the F-22 Raptor have been a source of ongoing discussion, especially given the aircraft’s advanced capabilities and the unique maintenance and training requirements it entails.
Key Operational Cost Factors
- Maintenance: The F-22’s stealth coating and specialized components require regular maintenance, often performed by highly trained personnel.
- Training and Simulators: Pilot training for the F-22 is extensive and involves advanced simulators and training programs, adding to the operational costs.
- Logistics and Support: Ensuring the aircraft’s availability and readiness involves a complex logistics network and support structure.
- Upgrades and Modernization: The Air Force has committed to continuous upgrades to keep the F-22 at the forefront of fighter technology, incurring additional costs.
| Estimated Annual Operational Cost per F-22 | $25-30 million |
|---|---|
| Total Operational Costs (Estimated over 30 years) | $10-12 billion |
Cost-Effectiveness and Future Implications
The F-22 Raptor’s overall cost, which includes development, production, and operational expenses, has been a subject of debate, especially considering the relatively small number of aircraft produced. However, proponents of the F-22 argue that its capabilities, including its stealth, supercruise, and advanced avionics, make it a formidable asset, justifying the investment.
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
The cost-effectiveness of the F-22 can be assessed by considering its performance and capabilities relative to its costs. While the aircraft’s development and production costs were high, its operational capabilities and the strategic advantage it provides to the US Air Force are often cited as justifications for its expense.
The F-22's stealth capabilities, for instance, allow it to penetrate enemy air defenses and conduct precision strikes with minimal risk of detection. Its supercruise ability enables it to maintain supersonic speeds without afterburners, providing a significant advantage in speed and fuel efficiency over non-supercruise aircraft.
Furthermore, the F-22's advanced avionics and sensor fusion systems provide pilots with an unprecedented situational awareness, enabling them to make critical decisions rapidly. These capabilities, combined with the aircraft's high maneuverability and advanced weaponry, make the F-22 a formidable asset in both air-to-air and air-to-ground roles.
Future Implications and Considerations
The F-22’s high cost has led to discussions about its long-term viability and the potential need for alternative aircraft. However, the Air Force has committed to maintaining the F-22 fleet, citing its unique capabilities and the strategic advantage it provides.
The F-22 program has also had significant technological spinoffs, with many of the advancements developed for the F-22 being applied to other military and civilian technologies. This includes advancements in stealth materials, advanced manufacturing techniques, and avionics, which have found applications in other aircraft, unmanned systems, and even commercial technologies.
As the Air Force continues to invest in the F-22's modernization and upgrades, the aircraft is expected to remain a critical component of the US military's air power for the foreseeable future. Its advanced capabilities and the strategic advantage it provides are seen as justifications for its continued operation and maintenance.
How does the F-22’s cost compare to other advanced fighter jets?
+The F-22’s cost is significantly higher than many other advanced fighter jets. For instance, the F-35 Lightning II, another stealth fighter, has a much lower production cost per unit. However, the F-22’s unique capabilities, including its supercruise and advanced avionics, make it a more specialized and expensive platform.
What are the key benefits of the F-22’s advanced capabilities?
+The F-22’s advanced capabilities provide a range of benefits, including stealth for penetrating enemy air defenses, supercruise for rapid response and increased range, and advanced avionics for enhanced situational awareness. These capabilities give the F-22 a significant advantage in modern air warfare.
How does the F-22’s cost impact the US Air Force’s budget and strategy?
+The F-22’s high cost has a significant impact on the Air Force’s budget and strategy. The aircraft’s development, production, and operational costs have required substantial resources, which has influenced the Air Force’s acquisition and modernization plans for other platforms. The F-22’s strategic importance, however, has justified its continued support and funding.