Define Group Norms
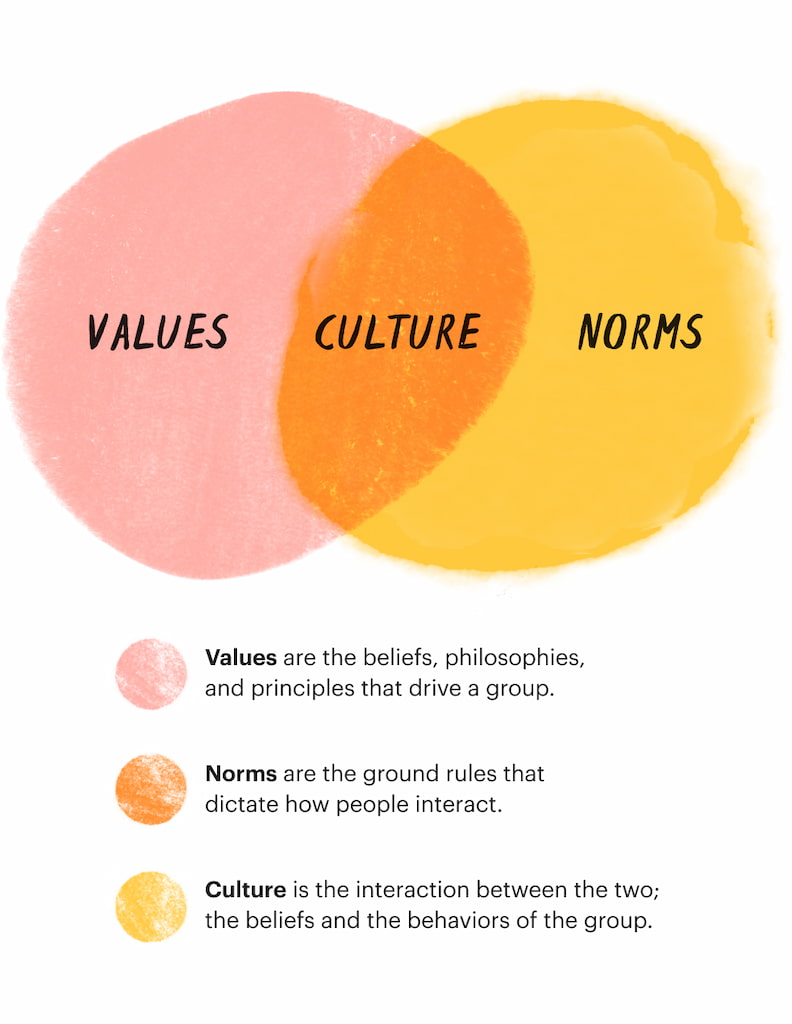
Group norms are the unwritten rules, expectations, and standards that govern the behavior and interactions within a particular social group or team. These norms are established through shared understanding and consensus among group members and serve as guidelines for appropriate conduct, decision-making, and overall group dynamics.
The Formation and Purpose of Group Norms

Group norms evolve organically as individuals within a collective setting interact and communicate. They are shaped by the group’s values, goals, and cultural context, ensuring that the group functions harmoniously and efficiently. These norms are not explicitly stated or formally documented but are implicitly understood and adhered to by all members.
The primary purpose of group norms is to maintain order, cohesion, and productivity within the group. By establishing these unwritten rules, members know what behaviors are acceptable and what behaviors are discouraged. This fosters a sense of unity, trust, and mutual respect among group members, enabling them to work together effectively towards shared objectives.
Examples of Group Norms
Group norms can vary widely depending on the specific context and nature of the group. Here are some common examples of group norms across various settings:
- Meeting Etiquette: In professional environments, group norms may include punctuality, active participation, and respect for others’ time during meetings.
- Communication Style: Norms can dictate the preferred communication channels (e-mail, instant messaging, or face-to-face) and the expected response times for messages.
- Decision-Making Processes: Groups may establish norms for how decisions are made, such as consensus-building or majority voting.
- Conflict Resolution: Norms can guide how members handle disagreements and conflicts, promoting constructive dialogue and minimizing personal attacks.
- Workplace Culture: Norms can define appropriate behavior in the office, including dress codes, social interactions, and professional etiquette.
- Social Groups: In social settings, norms might dictate the expected level of formality, the use of respectful language, and the boundaries for personal space.
- Academic Groups: For student study groups, norms could involve equal participation, sharing of resources, and mutual support.
It's important to note that group norms can evolve over time as the group's dynamics and circumstances change. New members may bring their own perspectives and experiences, influencing the existing norms. Additionally, external factors, such as organizational changes or societal shifts, can also impact group norms.
The Impact of Group Norms on Behavior

Group norms have a significant influence on individual behavior within the group. Members often conform to these norms to fit in, avoid conflict, and maintain a positive group image. This phenomenon, known as normative influence, is a powerful force in social psychology.
When individuals join a group, they tend to observe and adopt the behaviors and attitudes that are deemed acceptable by the group. This conformity can lead to a sense of belonging and acceptance, but it can also limit individual expression and creativity. Striking a balance between adhering to group norms and fostering individuality is crucial for a healthy and dynamic group environment.
The Benefits and Challenges of Group Norms
Group norms offer several advantages, including:
- Cohesion: Norms promote a sense of unity and shared identity among group members, fostering a positive and supportive environment.
- Efficiency: Clear norms streamline decision-making processes and reduce conflicts, allowing the group to focus on its objectives.
- Consistency: Norms provide a framework for consistent behavior, ensuring that interactions and work processes are predictable.
However, group norms can also present challenges. For instance, strict adherence to norms may hinder innovation and adaptability. Additionally, certain norms may unintentionally discriminate against or marginalize certain group members, leading to feelings of exclusion or unfairness.
Conclusion
Group norms are an essential aspect of social dynamics, shaping the behavior and interactions within a group. While they provide structure and cohesion, it is crucial to periodically evaluate and adapt these norms to ensure they align with the group’s evolving needs and values. By understanding and effectively managing group norms, leaders and group members can create a positive, inclusive, and productive environment.
How are group norms established within a team or organization?
+Group norms are typically established through a combination of explicit and implicit processes. Explicitly, norms can be defined and communicated by group leaders or during team-building activities. Implicitly, norms emerge as group members interact and observe each other’s behaviors. Over time, consistent behaviors become recognized as norms.
Can group norms change over time?
+Yes, group norms are dynamic and can evolve as the group’s dynamics, goals, and external circumstances change. New members, leadership changes, or significant events can all influence the evolution of group norms.
How do group norms impact group productivity and performance?
+Well-defined and positively aligned group norms can enhance group productivity and performance by promoting cohesion, efficient decision-making, and a shared sense of purpose. However, overly restrictive or outdated norms can hinder creativity, adaptability, and individual initiative.