When Was Hydrogen Discovered?

Hydrogen, the simplest and most abundant element in the universe, has a fascinating history of discovery and exploration. Its unique properties and role in various scientific fields make it a subject of great interest and significance. Let us delve into the intriguing journey of hydrogen's discovery and its impact on our understanding of the world.
The Early Insights: Unveiling the Presence of Hydrogen

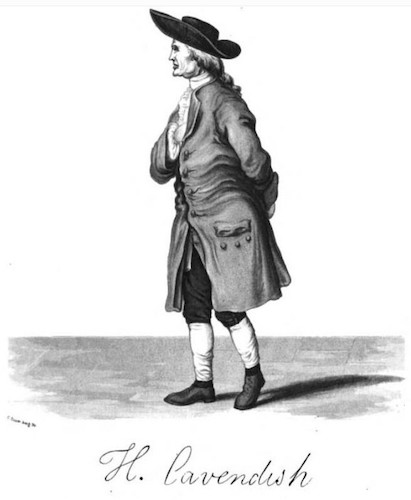
The story of hydrogen’s discovery begins in the 16th century, marked by a series of remarkable scientific observations and breakthroughs. It was during this period that scientists began to unravel the mysteries of gases and their properties. One of the key figures in this early exploration was Henry Cavendish, an English scientist renowned for his contributions to chemistry and physics.
Cavendish's experiments with "inflammable air," as he called it, laid the foundation for our understanding of hydrogen. In 1766, he observed that when a metal, such as iron or zinc, is reacted with certain acids, a highly flammable gas is released. This gas, which we now know as hydrogen, had the unique ability to produce a bright flame when ignited. Cavendish's work not only identified hydrogen's existence but also hinted at its potential as a powerful energy source.
The Birth of a New Element: Formal Recognition

It was not until 1783 that hydrogen was officially recognized as a distinct element. Antoine Lavoisier, a French chemist and one of the pioneers of modern chemistry, played a pivotal role in this recognition. Lavoisier’s meticulous experiments and his rejection of the phlogiston theory, which had dominated scientific thought at the time, led him to conclude that hydrogen was a unique substance with its own properties.
In a groundbreaking experiment, Lavoisier combined hydrogen with oxygen, producing water. This simple yet profound discovery not only confirmed hydrogen's status as an element but also showcased its remarkable ability to form compounds with other elements. Lavoisier's work laid the groundwork for our understanding of chemical reactions and the composition of matter.
Unveiling Hydrogen’s Secrets: Early Research and Exploration
Following its official recognition, hydrogen became a subject of intense scientific curiosity. Researchers delved deeper into its properties, exploring its behavior under different conditions and its potential applications. One of the most significant discoveries during this period was made by Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac, a French chemist and physicist.
In 1809, Gay-Lussac conducted a series of experiments to study the volume relationships in gas reactions. His findings, known as Gay-Lussac's Law, provided valuable insights into the behavior of gases, including hydrogen. This law stated that at constant pressure, the volume of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature. Gay-Lussac's work not only contributed to our understanding of gas behavior but also paved the way for further exploration of hydrogen's unique properties.
Hydrogen’s Impact on the Industrial Revolution
As the Industrial Revolution gathered pace, hydrogen found its place as a vital component in various industries. Its ability to produce a clean and efficient flame made it an ideal choice for lighting and heating applications. In the early 19th century, Friedrich Accum, a German chemist and inventor, developed the first hydrogen gas lighting system, revolutionizing indoor lighting and setting the stage for the widespread adoption of gas lighting.
Furthermore, hydrogen's role in the development of the hydrogen fuel cell cannot be overstated. This technology, which combines hydrogen and oxygen to generate electricity, has the potential to revolutionize the way we power our vehicles and devices. While the concept of the fuel cell was first proposed in the 19th century, it was not until the 20th century that significant advancements were made, leading to its practical application in various industries.
Modern Understanding and Applications: Hydrogen’s Endless Potential
Today, hydrogen continues to captivate scientists and researchers with its vast array of applications and potential. Its lightweight nature and high energy density make it an attractive option for energy storage and transportation. Hydrogen fuel cells, for instance, are being explored as a clean and sustainable alternative to traditional fossil fuels, offering the promise of a greener and more efficient future.
Moreover, hydrogen's unique properties have found their way into various industrial processes. It is used in the production of ammonia for fertilizers, as a reducing agent in metallurgy, and even as a rocket propellant in space exploration. The versatility of hydrogen knows no bounds, and its role in shaping the future of energy and technology is undeniable.
The Promise of Hydrogen: A Sustainable Future
In recent years, hydrogen has gained significant attention as a key player in the transition towards a sustainable and low-carbon economy. Its ability to store and transport energy without emitting greenhouse gases makes it an ideal candidate for a clean energy future. Governments and industries worldwide are investing in hydrogen technologies, aiming to harness its potential to reduce our carbon footprint and combat climate change.
The development of a hydrogen economy, where hydrogen is produced, stored, and utilized on a large scale, holds the promise of a more sustainable and resilient energy system. From powering vehicles to generating electricity, hydrogen has the potential to revolutionize the way we live and work, offering a cleaner and more environmentally friendly alternative to traditional energy sources.
The Future of Hydrogen: A World of Possibilities
As we look towards the future, hydrogen’s journey is far from over. Ongoing research and development are pushing the boundaries of what we know and what we can achieve with this remarkable element. From advancements in hydrogen storage and transportation to the integration of hydrogen into our daily lives, the possibilities are endless.
Imagine a world where hydrogen-powered vehicles dominate our roads, reducing air pollution and our reliance on finite fossil fuels. Picture a future where hydrogen fuel cells power our homes and businesses, providing clean and reliable energy. The potential of hydrogen to transform our energy landscape and contribute to a more sustainable world is both exciting and inspiring.
In conclusion, the discovery and exploration of hydrogen have taken us on a remarkable journey, from the early insights of Cavendish to the cutting-edge technologies of today. Its unique properties and vast potential continue to captivate scientists and researchers, driving innovation and shaping the future of energy and technology. As we continue to unlock the secrets of hydrogen, we move closer to a world powered by clean, sustainable, and abundant energy.
Who first discovered hydrogen?
+While Henry Cavendish made significant contributions to the understanding of hydrogen, it was Antoine Lavoisier who officially recognized hydrogen as a distinct element in 1783.
What are some modern applications of hydrogen?
+Modern applications of hydrogen include hydrogen fuel cells for clean energy production, ammonia synthesis for fertilizers, and its use as a reducing agent in metallurgical processes.
How is hydrogen produced for energy purposes?
+Hydrogen can be produced through various methods, including electrolysis of water, steam methane reforming, and biological processes. These methods aim to generate hydrogen in a sustainable and environmentally friendly manner.



