5 Quick Tips for Pronoun Agreement
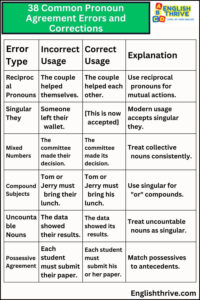
When it comes to the art of writing, ensuring pronoun agreement is an essential skill to master. It not only enhances the clarity and flow of your sentences but also demonstrates a deep understanding of the language. Pronoun agreement refers to the harmony between the antecedent (the noun the pronoun replaces) and the pronoun itself, ensuring they align in terms of person, number, and gender. This guide will provide you with five practical tips to achieve perfect pronoun agreement, making your writing more polished and professional.
Understand the Basics of Pronoun Agreement

The foundation of pronoun agreement lies in recognizing the types of pronouns and their functions. English pronouns can be classified into various categories, including personal pronouns (I, you, he, she, it, we, they), possessive pronouns (mine, yours, his, hers, its, ours, theirs), relative pronouns (who, whom, whose, which, that), and indefinite pronouns (each, either, neither, everyone, somebody). Each of these pronouns has specific rules for agreement, and understanding these rules is crucial.
For instance, personal pronouns must agree with their antecedents in number and gender. If the antecedent is singular, the pronoun must be singular; if the antecedent is plural, the pronoun should be plural. Similarly, if the antecedent is masculine or feminine, the pronoun should reflect the same gender.
Tip 1: Match Singular with Singular, Plural with Plural
One of the fundamental principles of pronoun agreement is maintaining consistency in number. This means that a singular antecedent should be followed by a singular pronoun, and a plural antecedent should be paired with a plural pronoun. For example, “The student completed his homework” (singular) versus “The students completed their homework” (plural). Paying attention to this detail ensures that your writing remains clear and avoids any confusion for your readers.
Tip 2: Be Aware of Gendered Pronouns
In English, some pronouns are gender-specific, such as he, she, him, and her. When using these pronouns, it’s essential to ensure they align with the gender of the antecedent. For instance, “The boy was happy because he received a gift” maintains the correct gender agreement. However, in cases where the gender is unknown or irrelevant, using gender-neutral pronouns like they, them, and their can be a more inclusive option.
Tip 3: Avoid Shifting Person and Number
When writing, it’s crucial to maintain consistency in the person and number of the pronouns used. Shifting from one person to another or changing the number mid-sentence can confuse readers and disrupt the flow of your writing. For example, “I love the way you cook” should not be followed by “and she does it so well.” Instead, maintain consistency: “I love the way you cook, and you do it so well.”
Tip 4: Use Care with Indefinite Pronouns
Indefinite pronouns, like each, either, every, and none, often present challenges in pronoun agreement. These pronouns can be singular or plural, depending on the context. For instance, “Every student submitted his or her assignment” (singular) versus “None of the students submitted their assignments” (plural). It’s important to analyze the context and choose the appropriate pronoun to ensure agreement.
Tip 5: Practice and Edit Thoroughly
Like any skill, mastering pronoun agreement requires practice. Write regularly and pay close attention to the agreement of your pronouns. Editing is also crucial; review your work carefully, checking for any instances of incorrect pronoun agreement. Tools like grammar checkers can be helpful, but nothing beats a thorough manual review to catch all the nuances.
| Pronoun Type | Example | Agreement Rule |
|---|---|---|
| Personal Pronouns | I, you, he, she, it, we, they | Match number and gender with antecedent |
| Possessive Pronouns | Mine, yours, his, hers, its, ours, theirs | Reflect ownership and match number |
| Relative Pronouns | Who, whom, whose, which, that | Agree with the antecedent in person and number |
| Indefinite Pronouns | Each, either, every, none | Determine context to decide singular or plural agreement |

What is an antecedent in pronoun agreement?
+
An antecedent is the noun that a pronoun replaces. In pronoun agreement, the antecedent and the pronoun must agree in person, number, and gender.
How can I identify gendered pronouns in my writing?
+
Gendered pronouns include he, she, him, and her. Look for these pronouns in your writing and ensure they align with the gender of the antecedent.
What are some common mistakes to avoid in pronoun agreement?
+
Common mistakes include shifting person and number within a sentence, using the wrong form of a pronoun (singular instead of plural or vice versa), and failing to match the gender of the antecedent with the pronoun.
How can I improve my pronoun agreement skills?
+
Practice writing regularly and pay close attention to pronoun agreement. Editing and proofreading your work carefully can also help you catch and correct any errors.
Are there any resources to help with pronoun agreement?
+
Yes, grammar guides, style manuals, and online resources can provide valuable insights and examples to help you improve your pronoun agreement skills.



